Natural Language Processing is Fun Part 4
GPT-2 has transformed text generation, producing output that is more realistic than ever before. OpenAI was so impressed by the quality of its text that they decided not to release the full GPT-2 model, fearing it could be misused to create misleading fake news that might deceive the public or overwhelm search engines like Google.
This raises a daunting question: how easy is it for the average person to generate fake news that could convincingly trick real readers? Let’s explore the capabilities of systems like this and consider the threats they pose.
Creating a Fake News Website
To visualize our findings, we’ll build a fictitious newspaper called “News You Can’t Use,” showcasing AI-generated content.

We’ll create a Python script to mimic a news site like the New York Times, generating artificial news stories while assessing the quality of the output and discussing the ethical dilemmas this technology introduces.
Understanding GPT-2’s Capabilities
GPT-2 is immensely knowledgeable due to being trained on vast amounts of text from the internet. It generates realistic sentences based on this knowledge. For example, starting with the text “Abraham Lincoln” might yield a response containing plausible yet false historical details.
This ability stems from two main factors: the scale of the model (1.5 billion parameters) and the innovative Transformer architecture it utilizes.
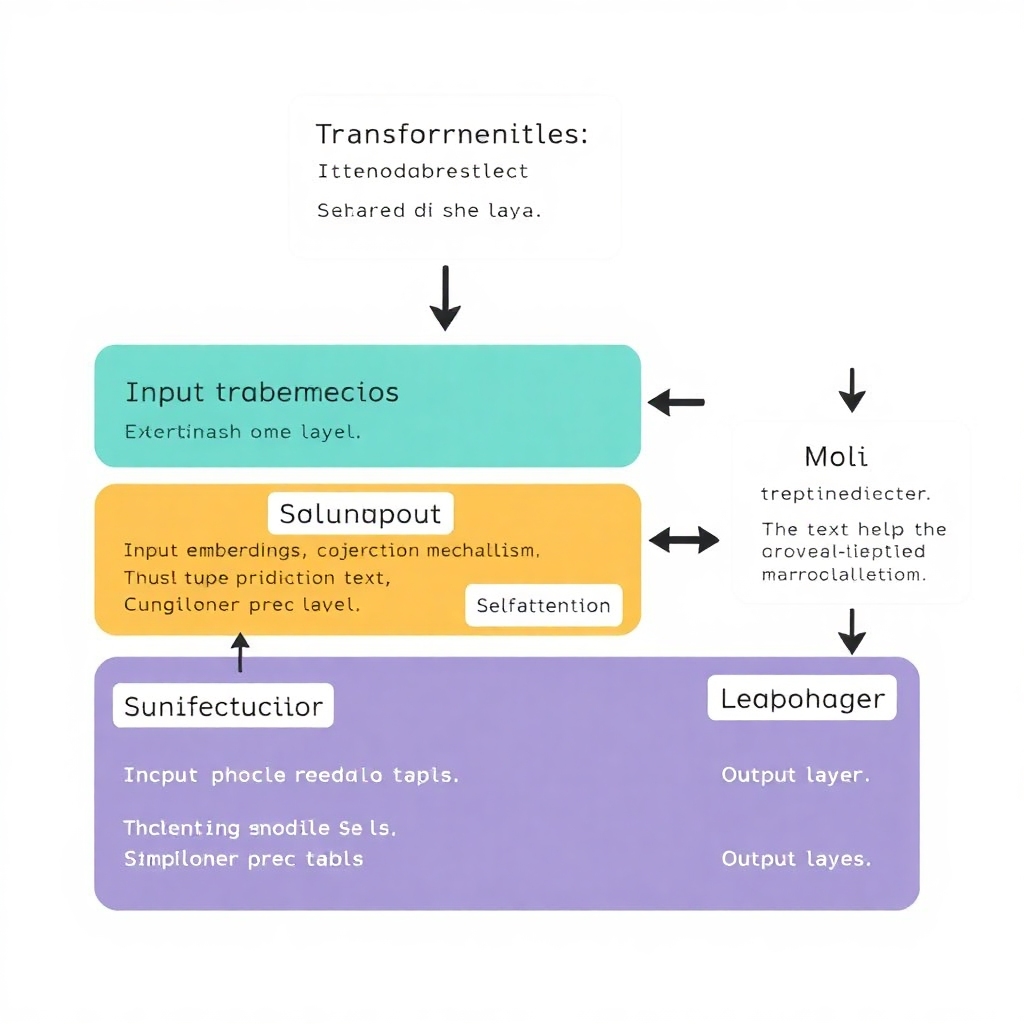
How GPT-2 Works
The architecture relies on context and statistical modeling rather than a straightforward database of facts. Older models, like Bag of Words, fail to grasp the sequence and context of words, which is crucial for human language.
In contrast, RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) improved this by processing words in sequence. However, they struggled with longer texts until the Attention mechanism was introduced, allowing models to focus on specific words.
Transformers, the foundation of GPT-2, utilize this concept further, maintaining contextual awareness across entire paragraphs. They model text significantly more efficiently than RNNs, enabling better coherence and relevance in generated text.
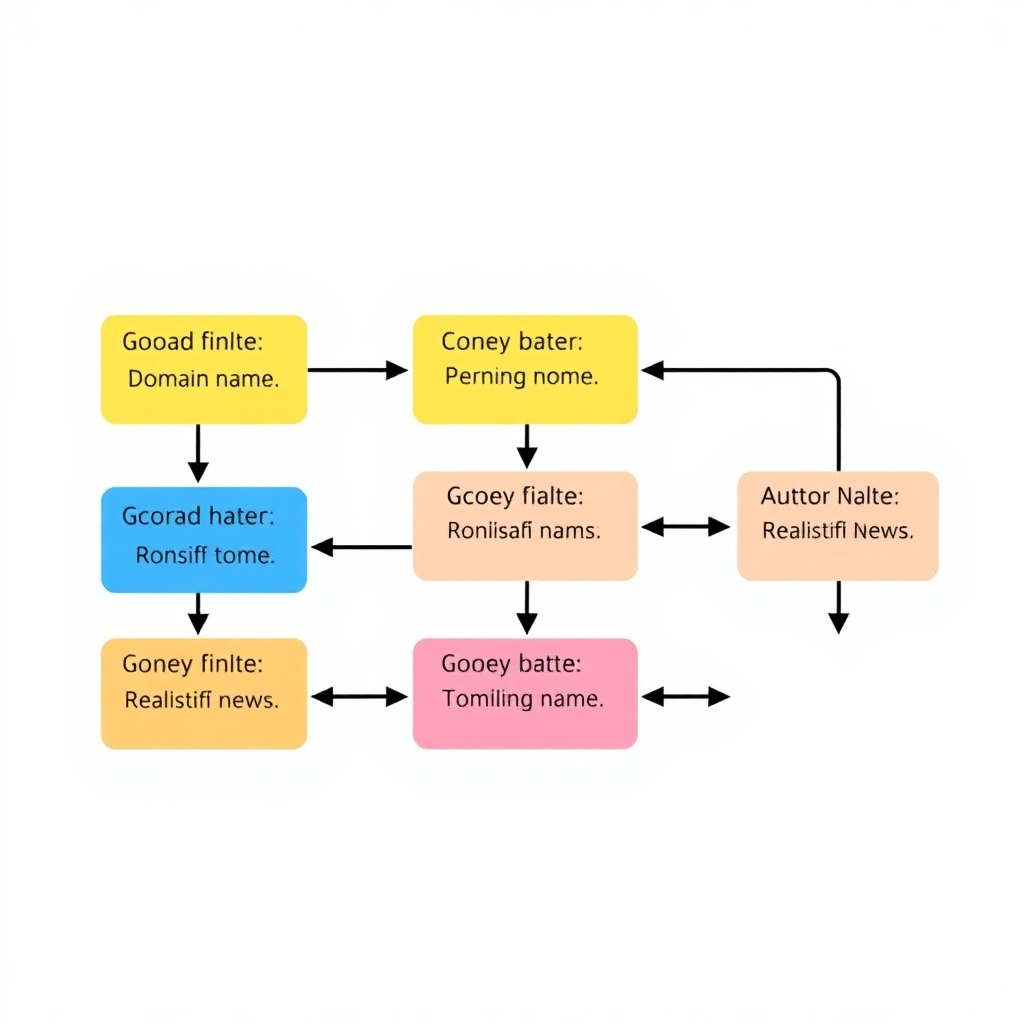
Grover: Better Control Over News Generation
To generate fake news articles responsibly, we can use Grover, which builds on GPT-2. Grover understands contextual elements like headlines and author names, enabling it to produce coherent and related outputs.
It models news stories as having distinct components:
- Domain name (e.g., nytimes.com)
- Author name
- Date published
- Headline text
- Body text
This knowledge allows Grover to generate realistic articles based on specific headlines.
The Implications and Ethical Considerations
While GPT-2 and similar models represent exciting advancements in machine learning, they carry risks of misuse. There’s a growing conversation around how best to manage and regulate their capabilities. Despite OpenAI’s initial decision to restrict access, researchers have since reproduced the model with alarming ease.
Ultimately, these technologies can either propagate misinformation or aid in the fight against it. Grover, originally designed for news generation, proves to be equally effective in fake news detection—demonstrating the potential for dual-purpose applications in combatting misinformation.
As the generation of fake news becomes increasingly sophisticated, it’s critical for creators and platforms alike to develop mechanisms for accountability and transparency, ensuring ethical usage of such powerful tools.
Feel free to reach out if you need any further adjustments or additional content!
